2020 Blog, AIOps Blog, Blog, Featured
Infrastructure Automation using Terraform
With growing Cloud adoption and need for Intelligent Infrastructure Automation, larger enterprises are adopting Hybrid-Cloud solutions like Terraform. Creating reusable templates for provisioning of complex infrastructure setups in Cloud and Data Centers, Orchestrating Cloud management with self-service Portals and full lifecycle monitoring of the assets can provide a flexible, reusable and scalable enterprise cloud solutions.
Relevance Lab is a Hashicorp partner with multiple successful enterprise infrastructure automation implementations using Terraform covering AWS, Azure, VMWare and GCP with 5000+ nodes setups.
Solution Highlights:
- Our solution allows you to rebuild stacks using automation completely. It is instrumental in provisioning newer environments with minimal code changes.
- It has the built in ability to replicate stacks across multiple regions with minimal code changes.
- Capability to add / remove new instances to components with few code changes.
- Simple code structure. Any new infrastructure needs can be easily provisioned by modifying the variables.
- Ability to modify instances such as Volumes, Instance Sizing, AMI changes, Security groups with minimal code changes.
Tools & Technologies:
Terraform from HashiCorp has emerged as the best Infrastructure automation tool. Terraform helps in building, changing and versioning of the infrastructure efficiently. Terraform is a declarative and, with the help of configuration files, we can describe the components to be built and managed across the entire datacenter.
Design Considerations:
Below mentioned are some of our design considerations based on standard practices in infrastructure automation. These structures have helped us gain flexibility and ease in scaling stacks based on demand.
- Code Repo Structure:
- It makes the code design structure very scalable to create newer AWS stacks in a different region or re-build stacks in case of a disaster or scale more resources based on traffic/load.
- A separate repo helps in maintaining isolation as each stack would have varied footprints of the resources.
- It helps in security and compliance as audits can be performed against a specific stack.
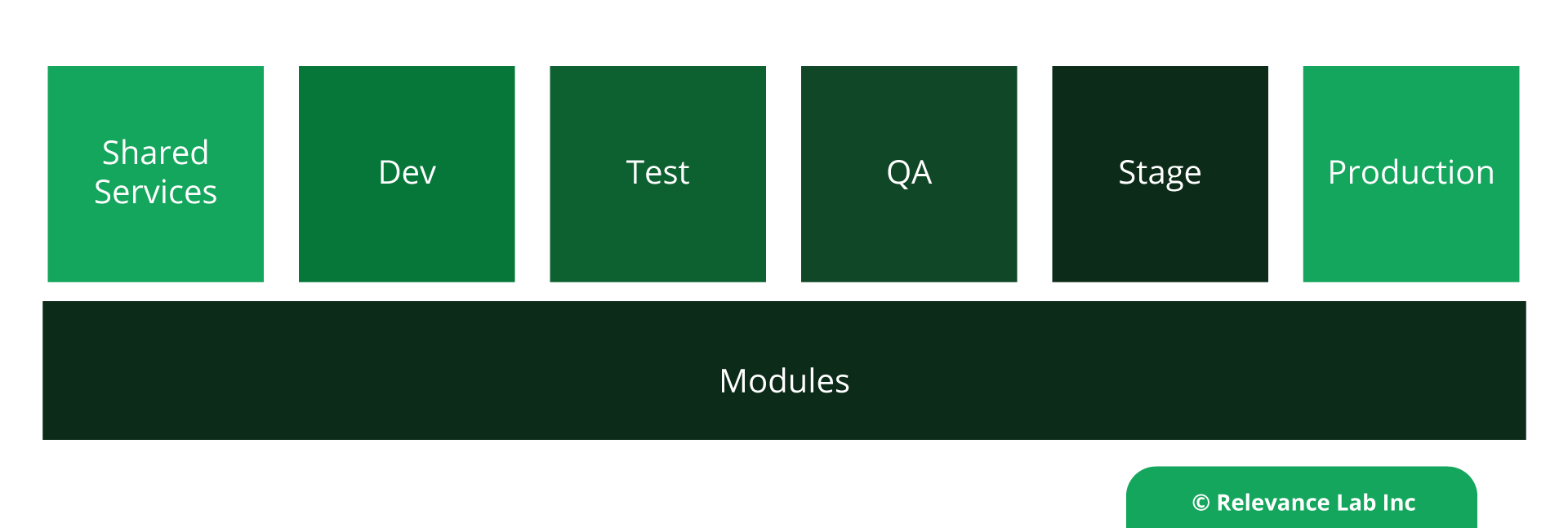
- Segmentation:
- Integration:
- Each change is performed on a branch which is merged via a Pull Request.
- Each Pull request is reviewed and verified and combined with the Master branch.
- Infrastructure changes are thoroughly tested during the PLAN stage and then terraform APPLY.
- Code reusability:
- Modules can help with this as they significantly reduce duplication, enable isolation, and enhance testability.
Each AWS stack is a separated GITHUB Repo while Terraform modules are a shared repo.
The below design model is showing the Automation build-out for each AWS account. Each layer is well segmented and can be easily scaled based on the needs. Making any specific change to each of the layers is easier.
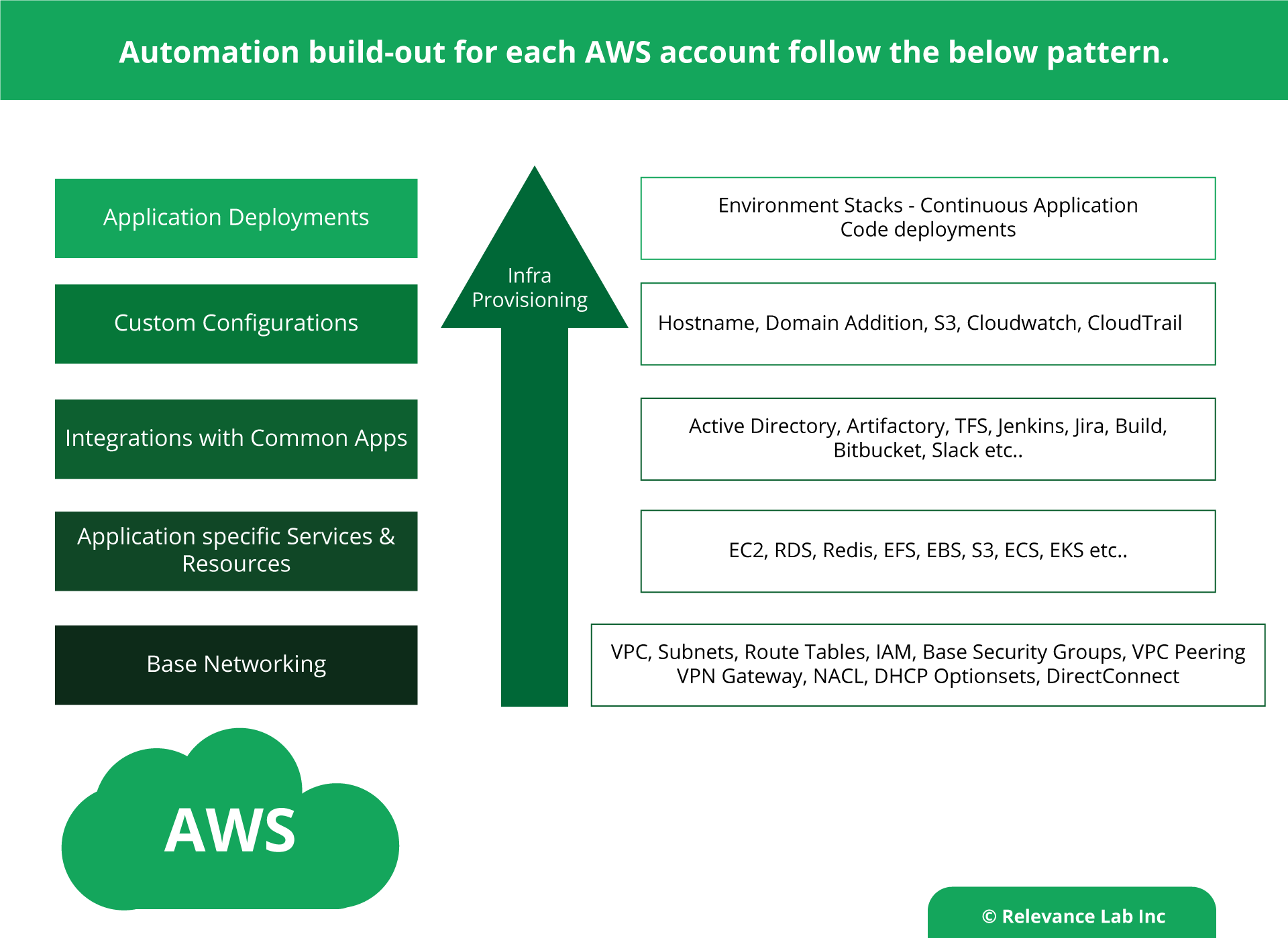
Fully integrated with GITHUB for Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment.
Modules provide an easy way to abstract, common blocks of configuration into reusable infrastructure elements.
Benefits:
- Provides the ability to spin up an entire environment in minutes.
- It reduces time to rollout complex network and storage changes to less than a few minutes.
- Infrastructure is managed as a code, and all changes are tested well; resulting in fewer outages because of infra configuration changes.
- It is easy to operate and maintain because terraform uses a declarative language.
- Infra is Idempotent, and a state-based desired system.
Conclusion:
Using design best practices of terraform, enterprises can quickly build and manage infrastructure, which is highly scalable and efficient. Further, this automation can be hooked to a Jenkins pipeline project for automated code pushes for infra changes which can be tied to a standard release and deployment process.
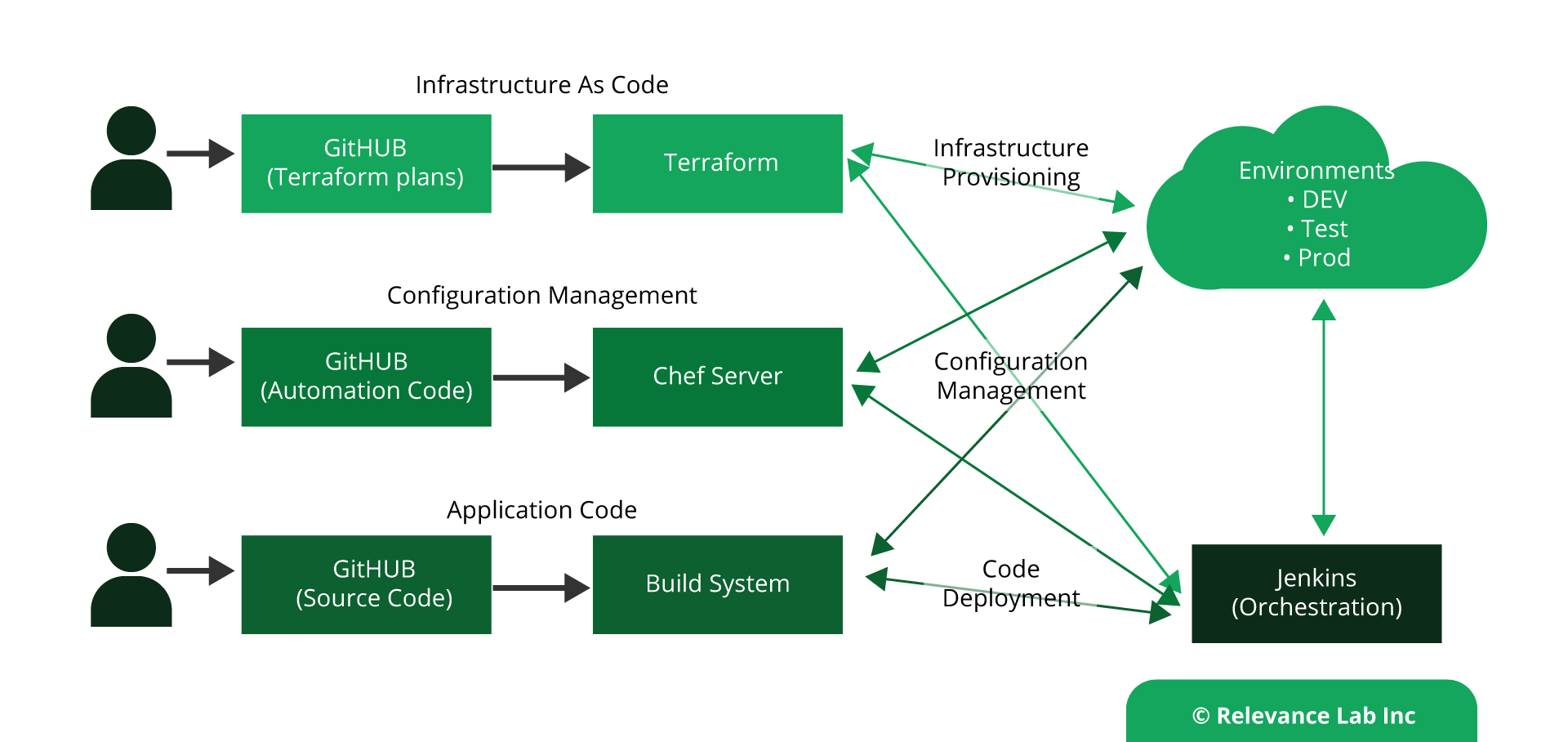
- Leveraging Chef for configuration management and managing all the application software installation and configurations via Chef cookbooks and recipes.
- Leveraging InSpec for auditing the properties of the AWS resources.
There are few other additions which could be introduced to this design to do a tight bonding between security and compliance policies and infrastructure as code. That may be achieved by integrating with Sentinel It helps in prevention of infra provisioning if there are deviations in the Infra code which do not adhere to the security policies. Sentinel helps us in building a fine-grained, condition-based policy framework.
For more details or enquires, please write to marketing@relevancelab.com


